Your Guide to Your Menstrual Cycle Without Taboos
Louloucup is here to answer all of your questions. No taboos or judgments here - just simple facts. Because yes, the female body goes through a complex process every month: The menstrual cycle!
How does a menstrual cycle work? 🩸
The menstrual cycle is a unique process in the female body. It starts during puberty. It’s essentially a hormonal phenomenon that lasts for decades until a woman reaches menopause. The menstrual cycle is what allows our bodies to become pregnant. Every month, your period prepares the uterus to receive sperm. If the egg is not fertilized, then the egg is destroyed and a new cycle starts again.
Let's get back to the basics:
An average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days. This is a large average because, in reality, very few women have such a precise period every month! Cycles can range from 21 and 45 days and still be considered normal.
The average 28-day cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase (from day 1 to day 14), which includes bleeding (period or menstruation) + 7 to 8 days when the endometrium prepares for potential fertilization, ovulatory phase (around day 14) is the point in the cycle when a woman has the best chance of getting pregnant, and finally the luteal phase (from day 15 to day 28) which stretches from ovulation until the day before the next period. This last phase is often linked to PMS.
Reminder: The first day of the cycle corresponds to the first day of menstruation; therefore, the last day turns out to be the day before the next menstruation!
Bleeding lasts on average between 2 to 5 days but some women may bleed for 7 days.

What hormones affect the menstrual cycle?
Menstruation is regulated by hormones in the brain. They send different messages that trigger bleeding, period symptoms, and premenstrual symptoms.
Before going any further, here is a little dictionary:
The ovarian follicles are kinds of "bags" that appear during menstruation in the ovary thanks to FSH. Each follicle contains an oocyte or ovum. Only one ovarian follicle matures. This elected official, named the Graafian follicle then releases the egg. This is the time of ovulation in the menstrual cycle. The follicles are essential in the process of procreation.
The yellow body is the result of the mature follicle bursting to release the egg at ovulation. Even empty, it still holds an important role. It secretes essential progesterone for the implantation of the egg in the uterine cavity if there is fertilization and for the triggering of the next period if there has been no fertilization.
FSH and LH
During menstruation, thepituitary gland, located in the skull, in thehypothalamus creates FSH, the follicle-stimulating hormone. As its name suggests, FSH stands for follicle stimulating hormone. The FSH's mission at each cycle is to increase the follicles in the ovary. Each follicle contains an egg. One follicle will become dominant and only one egg will mature. The other created follicles disappear.
Luteinizing hormone or LH is also produced by the brain. Its role is to release the egg.
Estrogen and progesterone
Estrogen and progesterone are female sex hormones. While estrogen is created by folliclesin the ovaries, progesterone is created by the yellow body. The corpus luteum is what remains of the follicle after ovulation. What are these hormones for during the menstrual cycle? These two hormones act on the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus or lining of the uterus in order to receive the fertilized egg.
The 3 phases of the menstrual cycle
The follicular phase (day 1 to 14)
The follicular phase is the first phase of the menstrual cycle and begins on the first day of menstruation. It typically lasts about XNUMX to XNUMX days but can vary from woman to woman. During this phase, multiple follicles in the ovaries begin to develop and mature under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) produced by the pituitary gland.
What is menstrual flow?
Your menstrual flow represents the intensity of your periods. Remember, every woman is different, so every menstrual flow is different. Also, different colors, flows, pain levels, and the duration of your period are common. When we talk about “normal” menstrual flow, we particularly talk about the flow we have once our menstrual cycle is established and stable. To give an idea, a menstrual flow represents, on average, between 2 to 5 tablespoons of blood or between 30 to 70 mL of blood per cycle.Here's a general guideline:
Light flow: 30 mL/cycle
Medium flow: 30 to 50 mL/cycle
Abundant flow: 50 to 70 mL/cycle
Very abundant flow, even hemorrhagic: more than 70 mL
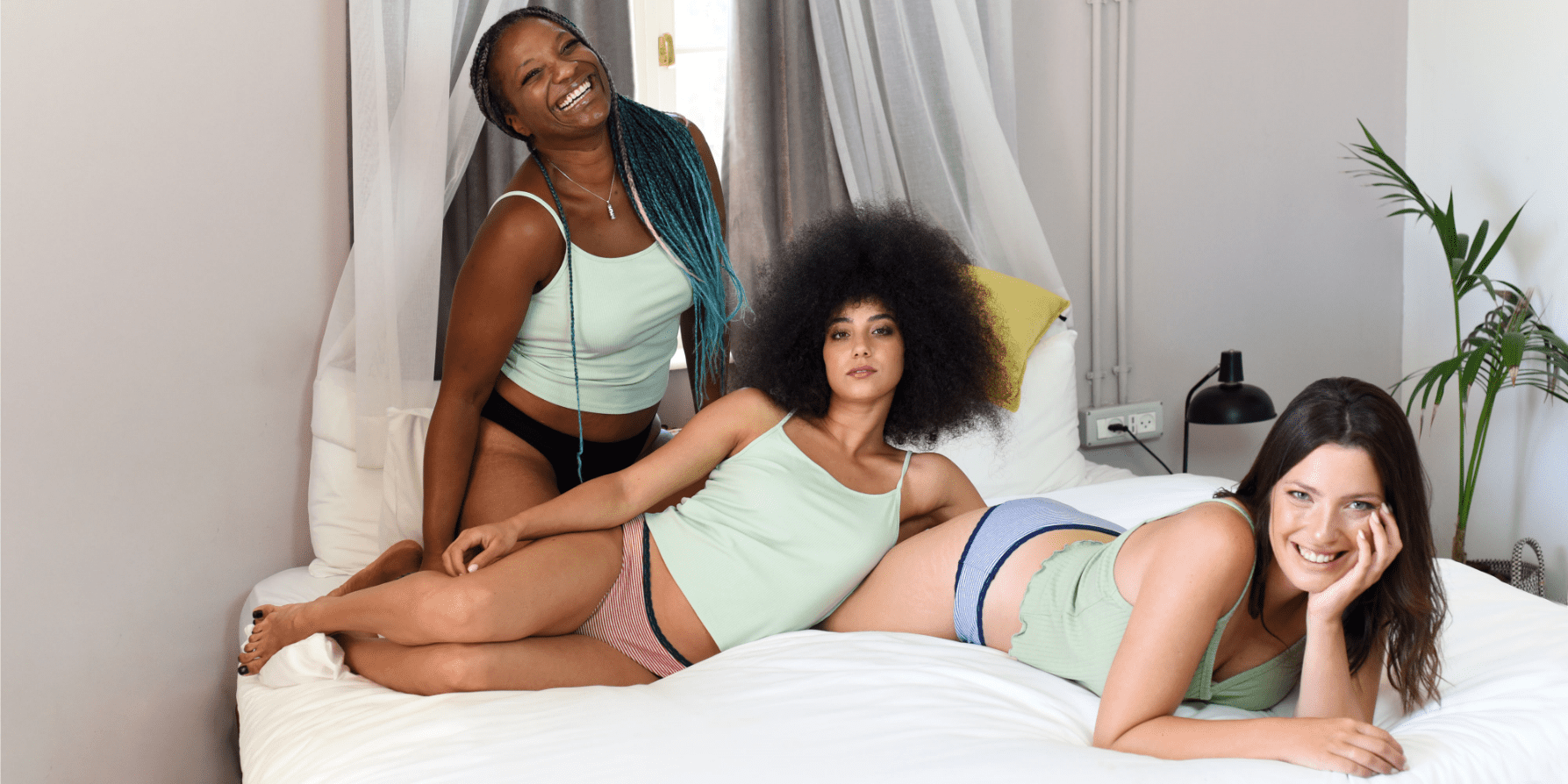
These are the benchmarks we use to determine the perfect cut and composition for our period panties.
It is completely normal to lose a lot of blood. That's why we use the menstrual cup to help determine how much blood we loose during a cycle.
Flow is usually heavier during the first two days of menstruation, with very red blood. Little by little, the color of the blood evolves to give way to more pink, brown, and or even black blood because the bleeding is lighter.
Some flows are more watery, while others can clot or be thicker. It depends on your body and where you're at during your cycle. But it's all normal!

???? All flow is normal. However, some things can impact your flow, like :
- Age
- Contraception
- Sress
- Some medications
Contraceptive hormones will tend to reduce the intensity of menstruation, while the copper IUD will tend to make it more abundant and more liquid.
So don't panic, it's normal! :)
Menstrual flow glossary 📖
Hemorrhagic flow
A very abundant or hemorrhagic flow is usually when the period lasts more than a week, and it is necessary to change sanitary protection every hour for several consecutive hours. If you think you are prone to hemorrhagic flows, consult a professional to rule out certain disorders.
Amenorrhea
This is when you don't have a period. This can be caused by eating disorders, intensive sports, certain medications, or certain diseases such as polycystic ovaries, thyroid problems, etc.
Oligomenorrhea
This is the term for light periods (less than 30 mL/cycle).
Spotting
Not to be confused with oligomenorrhea, spotting occurs as bleeding between periods, signifying a hormonal imbalance.

The ovulatory phase
The mature follicle has released the egg marking the end of the follicular phase. This is the starting signal for theovulation. For its part, thanks to estrogen and progesterone, the uterus is ready. The uterine lining is thick enough for the embryo to cling to - giving the green light for fertilization. The egg then takes about 24 hours to make its way between the ovary and the fallopian tube.
If the sperm meets, then fertilization has a good chance of succeeding. If the sperm doesn't meet, the egg continues its journey to the uterus to be dissolved there.
Physically, the ovulatory phase or period of ovulation happens as follows:
1. By the appearance of cervical mucus. Why? Because to accommodate the sperm, the cervix has to open slightly. Cervical mucus is essential for easier transportation of sperm into the uterus. So don't panic; it's completely natural to have vaginal discharge or white dischargeat the time of ovulation. Moreover, its texture and intensity evolve over the course of the cycle.
XNUMX. A rise in base temperature. Body temperature rises slightly to allow sperm to survive longer.
The Luteal Phase (Day 14 to 28 or more)
After ovulation, the period enters its last phase, the luteal period. The female body awaits fertilization and prepares itself. The yellow body is left behind by the mature follicle that produces progesterone again and again to prepare the endometrium. When a fertilized egg does not appear, the yellow body dies bringing with it a drop in progesterone and the signal to evacuate the endometrium. A new cycle can then begin.
It is during the luteal phase that we have PMS or premenstrual syndrome.
All about PMS 💫
Do you feel a little extra 'off' or emotional a few days before your period? Are you very irritated, or do you lack patience? Are you particularly swollen in the belly or chest? Are you on edge, sad, numb, or even depressed? Then you know premenstrual syndrome !
Premenstrual syndrome affects many menstruating women. These physical and psychological manifestations occur in the second part of the menstrual cycle. PMS is simply due to fluctuating hormones. It's nothing bad. Just a little annoying. If you have severe or debilitating PMS symptoms, you may have something called premenstrual dysphoric disorder.

The symptoms may be different for everyone:
irritability, anger, and bad mood
panic or anxiety attacks
depressed or gloomy mood
crying attacks
severe fatigue or lethargy
headaches
bloating
breast pain
Some women experience slight weight gain, difficulty concentrating, and also insomnia.
If you are prone to some of these symptoms, try to limit foods that are high in sugar and caffeine. Focus on physical activity that you enjoy to occupy your mind, relax, and generate endorphins (the happy hormone).
These symptoms are easy. It is important to listen to your body and stay calm. Knowing your cycle and how to calculate it can help manage your symptoms. Make a PMS log for at least two cycles tp help pinpoint symptoms.
Do you suffer a lot from PMS? Talk to your doctor! Your primary care doctor or gynecologistshould be able to help. Trust the health professionals to answer all your questions and offer solutions. Don't forget, from puberty, a gynecological follow-up is required every year to ensure you're in good health.
Your cycle can get disrupted
Your cycle can be disrupted for many reasons. It's important to learn how to trust and understand your body. It's common for a cycle to get out of order due to a specific medical treatment or illness. Periods may arrive late. It doesn't mean there's something wrong with you.
For example ovarian cysts can impact your cycle. Also, the mature follicle that's meant to release the egg may not release on the expected date. This is called a follicular cyst. This type of cyst impacts your cycle and can cause pain. However, it usually resolves on its own during subsequent periods. If you're unsure what's going on or experiencing significant pain, visit your gynecologist. They can do an ultrasound to check things out and prescribe painkillers for a few days.
It is completely normal to experience different cycles at any point in life. Not every period will be the same. Some factors that can impact a cycle include stress, psychological shock, a significant weight loss, playing sports at a very high level, and more. Starting contraception can disturb your cycle for a little while. No worries. Everything should be back to normal pretty quickly.
When should you worry? Take notice when you are in pain, when your cycles are very irregular, like too short or too long, and when you feel significant symptoms. Listen to your body, and above all, do not hesitate to seek advice from a doctor!
Understanding menstrual pain 💫
Coming back to menstruation, let's talk about something that most of us experience at least once, if not every month: menstrual pain. Painful periods are the worst.
Period pain happens when the uterus contracts to eliminate the uterine lining. Pain, like cramps, can diffuse into the pelvis, back, stomach, and even the thighs.
The intensity varies from one woman to another. Some women don't experience bad pain, while for others, the pain is so intense it leads to vomiting. Some women experience a severe lack of energy or find it hard to stand up and prefer to stay in bed.
Tips to help relieve menstrual pain:
Do a physical activity, play a sport, or go for a walk. It may not be obvious, but a little exercise session can help. The stimulated blood circulation and better oxygen levels cause endorphins to spread faster.
Relax the muscles with massages and different sources of heat. A hot bath and a hot water bottle can do wonders. We also love enjoying a hot cup of tea and taking it easy (without feeling guilty)!
We hope this guide helps you feel more comfortable with your menstrual cycle. Remember, we're all unique and there's no such thing as a one-size-fits-all approach to periods! The goal is to manage your period. Make your next cycle easier with teen period panties or a You can wear a menstrual cup ! Being prepared to face your period is essential!


